Introduction
The definition of history consists in what creates its conflicts. Empires have been destroyed through wars and nations experienced boundary transformations while humanity experienced enduring transformative changes in its course. The long-term impacts of a war determine its true significance over the most pressing immediate results. Through the process of fostering nationalism and a revolution of technological progress and governance systems, historical conflicts permanently reshape the nature of societies.
Knowledge regarding these conflicts serves both to study past events and reveals evolution patterns of human development amid chaos. These historical events provide us with an understanding about the intricate nature of power struggles and political systems as well as human survival instincts. This paper examines ten renowned historical battles that currently influence modern society.
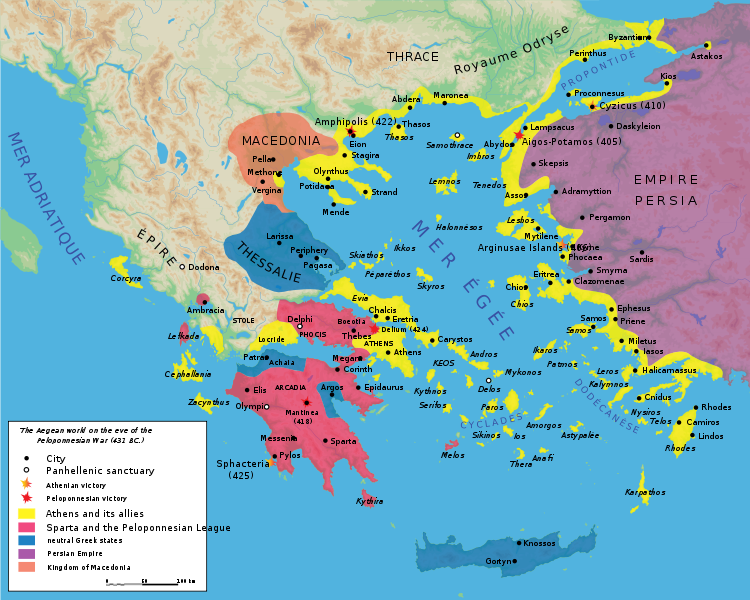
10. The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BCE)
Over 29 years two major ancient Greek city-states engaged in a prolonged battle as they fought at the beginning of the 5th century BC. A dispute for Greek world supremacy between ancient powers transformed into an exceptionally harsh battle that lasted for three decades. Athens maintained power through its naval supremacy while Sparta used its army discipline to become a militaristic nation.
Table of Contents
The Long-Lasting Effects:
The Greek world underwent decline during the time of this war. After being known as the cultural and democratic capital of the world Athens became defenseless against foreign incursions because of its military weakenin Sparta quickly lost its dominance to Macedonia after city-states within Greece started fighting among themselves which enabled Philip II and Alexander the Great to claim sovereign power. The war ended up showing how connected political relationships must be because prolonged warfare leads to destruction. The conflict motivated Thucydides to write History of the Peloponnesian War which continues to influence scholars who examine both warfare and human nature today.
9. The Punic Wars (264–146 BCE)
Rome together with Carthage engaged in three prolonged military confrontations to determine who would rule over the Mediterranean region. During the most well-known struggle Hannibal commanded his Carthaginian forces containing war elephants through the Alps to assault Rome.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
Rome took permanent control of dominion over the Mediterranean after its triumphs in the Punic Wars. When Carthage met its destruction at Roman hands during 146 BCE then Rome created its path to become an empire from being a republic. Rome secured vital trade networks during those conflicts while the military operations of those wars would impact strategy in the Roman armies for hundreds of years. Historians still refer to the statement Carthago delenda est (“Carthage must be destroyed”) as a prominent manifestation of total war because it defined military strategic thinking across numerous centuries.

8. The Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453)
During a span of 116 years France fought England in multiple wars due to disputes about control of the French royal authority. The prolonged conflict became infamous because Joan of Arc and the legendary Black Prince brought their influence to guide its historic events across one hundred years. The development of longbows together with knights losing their main military power became key changes that revolutionized medieval warfare.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
The conflict led to severe political and social transformations. Through the French conflict the nation created unified identity and increased royal power. England suffered from financial burdens in the war that eventually led to civil internal conflicts through the Wars of the Roses. The centralized emergence of monarchies in medieval society led to the decline of feudalism which had previously maintained medieval society. Military tactics involving gunpowder and innovative warfare practices marked the start of war systems that entered modern warfare.

7. The American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)
An important colonial uprising developed between Great Britain and American colonies since Americans fought to break free from British rule. The conflict extended far beyond freedom because the dispute encompassed taxation laws and representation rights and self-autonomy. Critical events consisting of the Boston Tea Party together with the Declaration of Independence promoted the colonies’ independence movement.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
Through its success America became the first-ever independent country that implemented democratic governance systems. Through its dissemination worldwide the American Revolutionary War motivated join movements toward independence such as both the French Revolution and all Latin American revolutions. Through the conflict America created its foundational U.S. Constitution that continues to function as the basis of modern governance even today. The historical shift in global trade power dynamics along with the establishment of liberty and equality principles as global cultural ideals occurred after this economic event.
6. The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815)
Napoleon Bonaparte initiated multiple wars to increase French domination across European countries in the Napoleonic Wars. His extensive military operations transformed the European continent through extensive political reforms and significant social transformation.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
After Napoleon’s defeat Europe’s leaders established the Congress of Vienna to reconfigure state borders as well as create a power sharing structure that would avoid future widespread conflicts. Through the Napoleonic Code which Napoleon developed into legal code many nations modified their laws. The war experiences of these nations during this period later became instrumental for their eventual unification. Total warfare where nations fully deploy their resources to fight became the main defining element of the Napoleonic Wars and all wars that followed.

5. The American Civil War (1861–1865)
The United States suffered its most significant internal conflict when the American Civil War unfolded in history. The Union (northern states) and the Confederacy (southern states) fought against each other while the war focused on slavery laws and states’ authority combined with preserving the United States as one nation. During this period Abraham Lincoln demonstrated essential leadership by announcing the Emancipation Proclamation.
Critical events consisting of the Boston Tea Party together with the Declaration of Independence promoted the colonies’ independence movement.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
Through its success, America became the first-ever independent country that implemented democratic governance systems. Through its dissemination worldwide the American Revolutionary War motivated joint movements toward independence such as both the French Revolution and all Latin American revolutions. Through the conflic,t America created its foundational U.S. Constitution which continues to function as the basis of modern governance even today. The historical shift in global trade power dynamics along with the establishment of liberty and equality principles as global cultural ideals occurred after this economic event.

4. The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815)
Napoleon Bonaparte initiated multiple wars to increase French domination across European countries in the Napoleonic Wars. His extensive military operations transformed the European continent through extensive political reforms and significant social transformation.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
After Napoleon’s defeat, Europe’s leaders established the Congress of Vienna to reconfigure state borders as well as create a power-sharing structure that would avoid future widespread conflicts. Through the Napoleonic Code which Napoleon developed into a legal code, many nations modified their laws. The war experiences of these nations during this period later became instrumental in their eventual unification. Total warfare where nations fully deploy their resources to fight became the main defining element of the Napoleonic Wars and all wars that followed.

3. The American Civil War (1861–1865)
The United States suffered its most significant internal conflict when the American Civil War unfolded in history. The Union (northern states) and the Confederacy (southern states) fought against each other while the war focused on slavery laws and states’ authority combined with preserving the United States as one nation. During this period Abraham Lincoln demonstrated essential leadership by announcing the Emancipation Proclamation. Three significant historical events during World War II were the Holocaust as well as the Battle of Stalingrad followed by the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
The war created significant changes to how nations big and small arranged their positions on the world stage. Alongside each other, the United States and Soviet Union surfaced as powerful nations which brought about the Cold War epoch. The United Nations was formed as an organization that seeks global peace through international cooperation to stop any forthcoming conflicts. The colonial powers began their territories’ release after experiencing exhaustion in wartime. Nuclear energy technology along with radar detection and aviation developments materialized because of World War II. The worldwide dedication to human rights became stronger after 1948 because the atrocities of the Holocaust prompted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.

2. The Cold War (1947–1991)
During an extended period which lasted from 1947 to 1991 the United States fought the capitalist version of its power against the Soviet Union’s communist governance. The indirect struggle between the US and the Soviet Union developed into proxy warfare while creating arms competition and boosting space exploration. Three major events during the Cold War period were the Cuban Missile Crisis combined with the Korean War and the Vietnam War.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
During the Cold War period, the world transformed into two distinct blocs consisting of Eastern and Western nations. The Warsaw Pact and NATO emerged together to protect the ideological goals of their members. Through space race competition scientists achieved numerous milestone accomplishments including achieving the first moon landing in 1969. After the Cold War ended with the collapse of the Berlin Wall and Soviet Union dissipation America became the sole ruling power in a one-polar world. Past Cold War competition generated lasting disruptions in areas throughout the Middle East and Southeast Asia.

1. The Vietnam War (1955–1975)
A major global conflict named the Vietnam War divided two opposing factions because North Vietnam received help from communist supporters while South Vietnam relied on the United States and anti-communist states. The conflict existed as part of the worldwide Cold War conflicts because U.S. leadership aimed to stop communist expansion.
The Long-Lasting Effects:
The conflict devastated Vietnam because it brought both significant destruction and collapsed the entire country’s economic system. American public confidence in government institutions suffered severe damage during the conflict which along with massive nationwide protests transformed both the national culture and political systems of the United States. During this conflict, the United States learned how their armed forces were unable to match certain objectives while worldwide perspectives shifted regarding colonial policies and foreign interventions. The eco-system in Vietnam experiences present-day effects from the Agent Orange chemical usage which was applied in the war. Through the conflict, the world experienced heightened inspiration for peace activism which contributes significantly to present-day activism.

Conclusion
Throughout history major wars in ancient Greek territories alongside contemporary global powers have established enduring consequences which direct international relationships in the present day. The resulting conflicts modified territorial lines while generating fresh countries and transforming the makeup of numerous populations. The experiences emphasized to us the value of warfare along with the fundamental value of establishing diplomatic connections. Researching these historic clashes teaches us significant understandings about both the past of humanity and our ongoing efforts to establish peace along with security stability.
Top 10 Lists of the people, things, places, most expensive, animals, most popular, luxury and high rankings of world. World's Top Insider focuses on the top ten lists of best, greatest and top rankings in the world.


